Level Goal
There is a git repository at ssh://bandit28-git@localhost/home/bandit28-git/repo. The password for the user bandit28-git is the same as for the user bandit28.
Clone the repository and find the password for the next level.
Solution
cloning the repo and listing the files in the working directory, we find README.md file, as we can see the credentials for user bandit29 is stored in this file, but the password filed contains aplaceholder not he password itself.
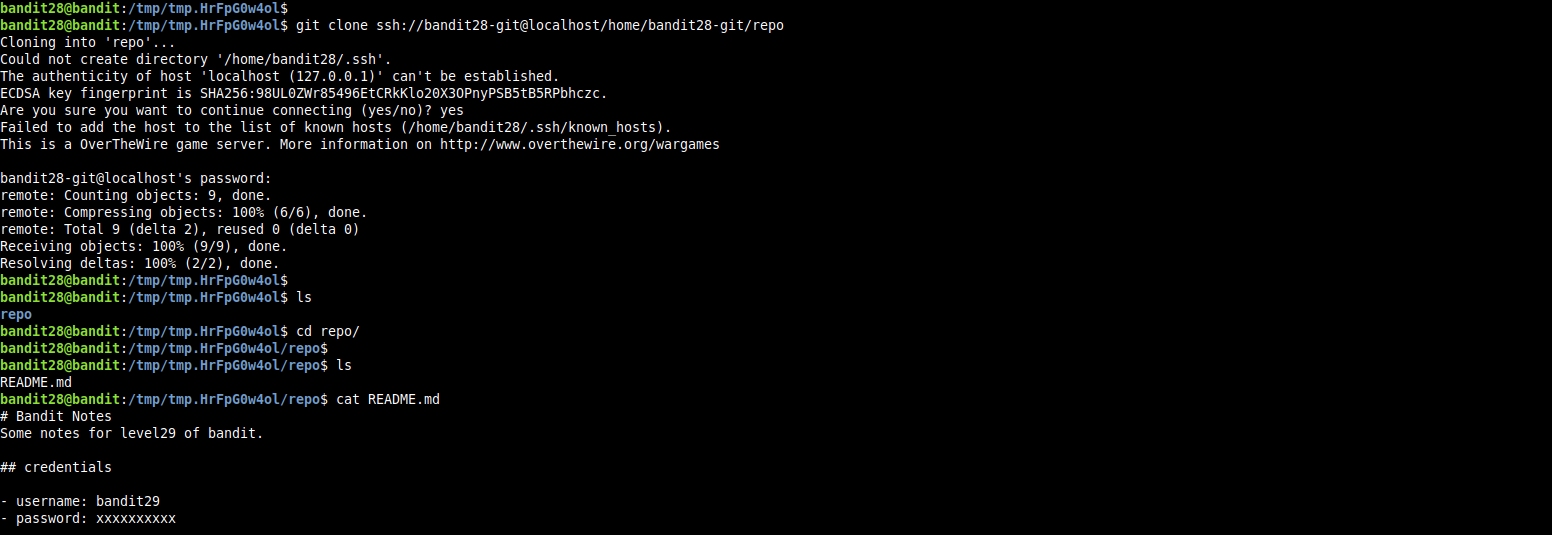
so, let’s get more informations about the versions of this file by viewing the commit history for this repository.
Read More
Level Goal
there is a git repository at ssh://bandit27-git@localhost/home/bandit27-git/repo. the password for user bandit27-git is the same as for the user bandit27.
clone the repository and find the password for the next level
Solution
cloning the repo provided in the level goal, and listing the files in the repo’s working directory we find a file named README.md.
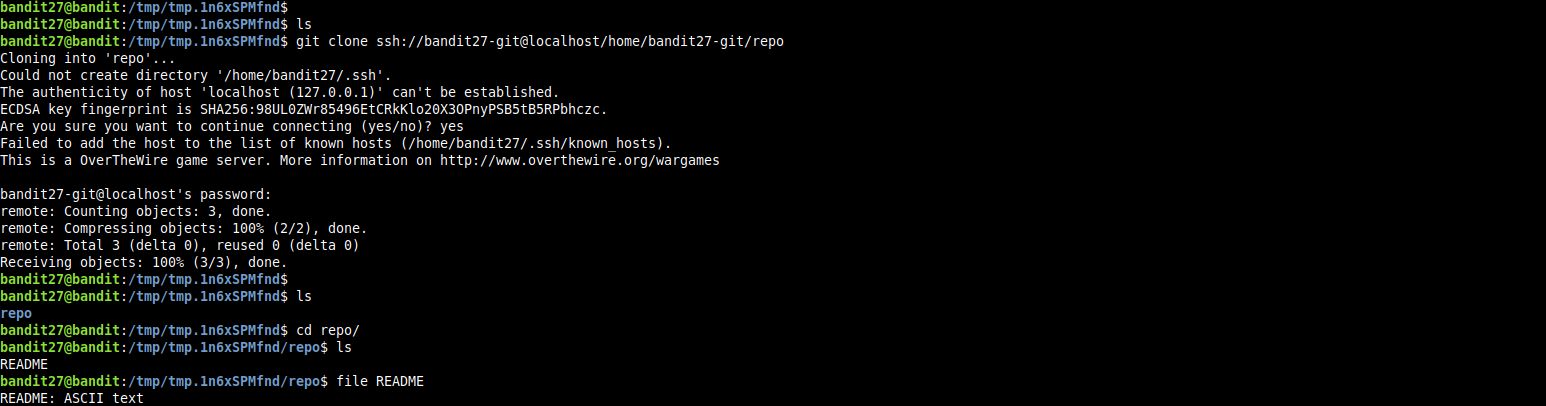
Read More
Level Goal
Good job getting a shell! Now hurry and grab the password for bandit27!
Solution
in the writeup for the previous level, we did get a shell as user bandit26, in the home directory for user bandit26 we found a file named bandit27-do, let’s get some information about this file.

Read More
Level Goal
logging in to bandit26 from bandit25 should be fairly easy… the shell for user bandit26 is not /bin/bash, but something else. find out what it is, how it works and how to break out of it
Solution
first let’s login to server as user bandit25, we will find the private key for user bandit26 which we will add to our ssh agent so we can log into the server as user bandit26.
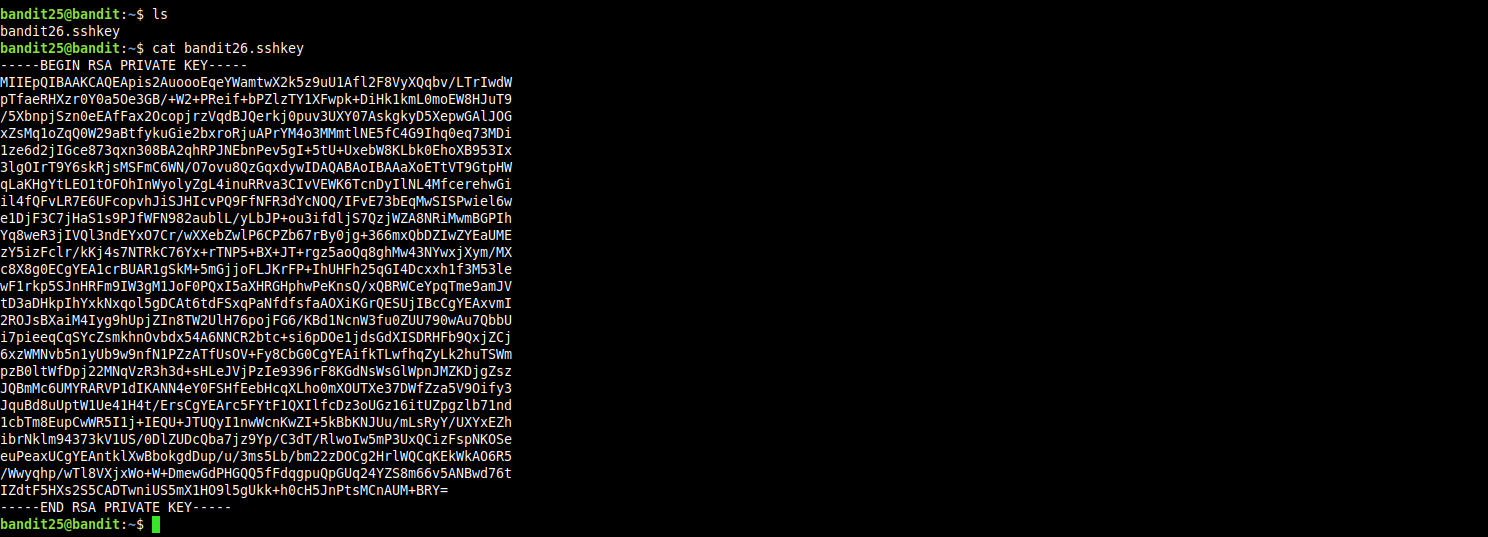
if we try to login as user bandit26 we will be presented with and ascii-art banner, then the session will be terminated immediately.

Read More
Level Goal
A daemon is listening on port 30002 and will give you the password for bandit25 if given the password for bandit24 and a secret numeric 4-digit pincode. There is no way to retrieve the pincode except by going through all of the 10000 combinations, called brute-forcing.
Solution
for this level i wrote the following bash script that will try to bruteforce the daemon running on port 30002.
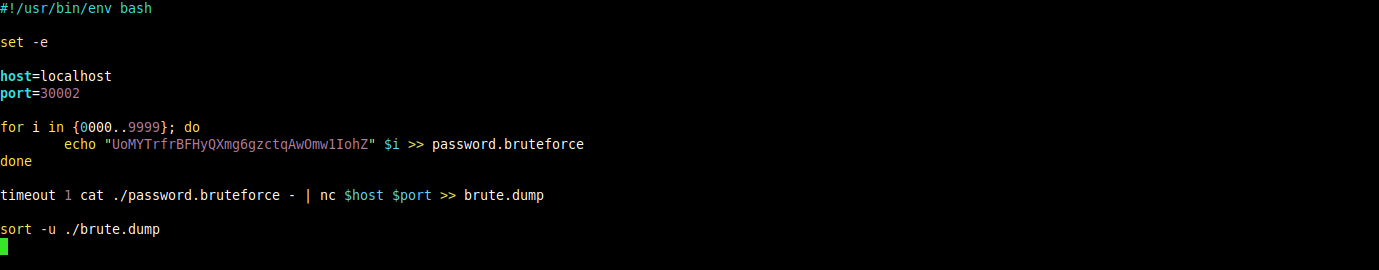
Read More
Level goal
a program is running automatically at regular intervals from cron, the time-based job scheduler. look in /etc/cron.d/ for the configuration and see what command is being executed.
NOTE: this level requires you to create your own first shell-script. this is a very big step and you should be proud of yourself when you beat this level!.
NOTE2: keep in mind that your shell script is removed once executed, so you may want to keep acopy around…
Solution
first we ls(1) the directory /etc/cron.d/.

as we can see the file cronjob_bandit24 is readable by any user, let’s see it’s contents.

Read More
Level Goal
a program is running automatically at regualr intervals from cron, the time based job scheduler. look in /etc/cron.d/ for the configuration and see what command is being executed.
NOTE: looking at shell scripts written by other people is very useful skill. the script for this level is intentionally made easy to read. if you are having problems understanding what it does, try executing it to see the debug information it prints.
Solution
let’s begin by ls(1) the /etc/cron.d/ directory

now we cat(1) the file named cronjob_bandit23 and see if it contains tasks for user bandit23.

we can see that the cron service will run file /usr/bin/cronjob_bandit23.sh every minute, so let’s get some information about this file.
Read More
Level Goal
a program is running automatically at regualr intervals from cron, the time-based job scheduler. look in /etc/cron.d/ for the configuration and see what command is being executed
Solution
first we ls(1) the directory that contain the system wide crontab files, usually they are located in /etc/cron.d/ and /etc/crontab/ directories, and can be edited only by the system administrator

Read More
Level Goal
there is a setuid executable in the homedirectory that does the following: it makes a connection to localhost on the port you specify as a commandline argument. it then reads a line of text from the connection and compares it to the password in the previous level (bandit20). if the password is correct, it will transmit the password for the next level (bandit21).
Solution
this challenge is all about shell job control.
Read More
Level Goal
to gain access to the next level, you should use the setuid binary in the homedirectory. execute it without arguments to find out how to use it. the password for this level can be found in the usual place (/etc/bandit_pass), after you have used the setuid binary.
Solution
a setuid in the unix world is a type of permission which when applied to an executable will give the user who executes it the same privileges of the executable owner. speaking unix, when a process is created from this executable it’s effective user id will be set to be equal to the id of the executable owner.
as stated in the level description, we will find out how to use this setuid executable if we executed it with no arguments.

Read More











